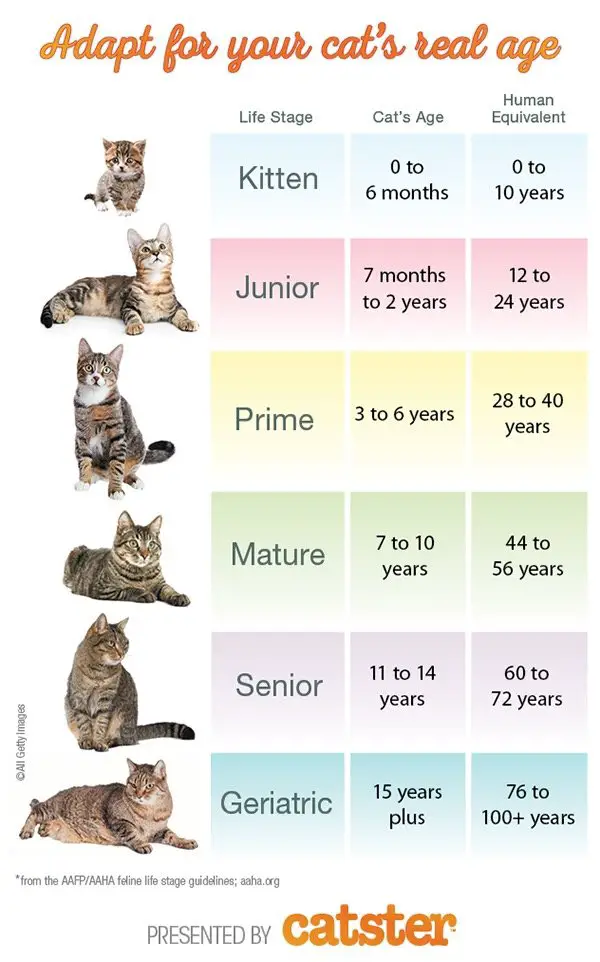
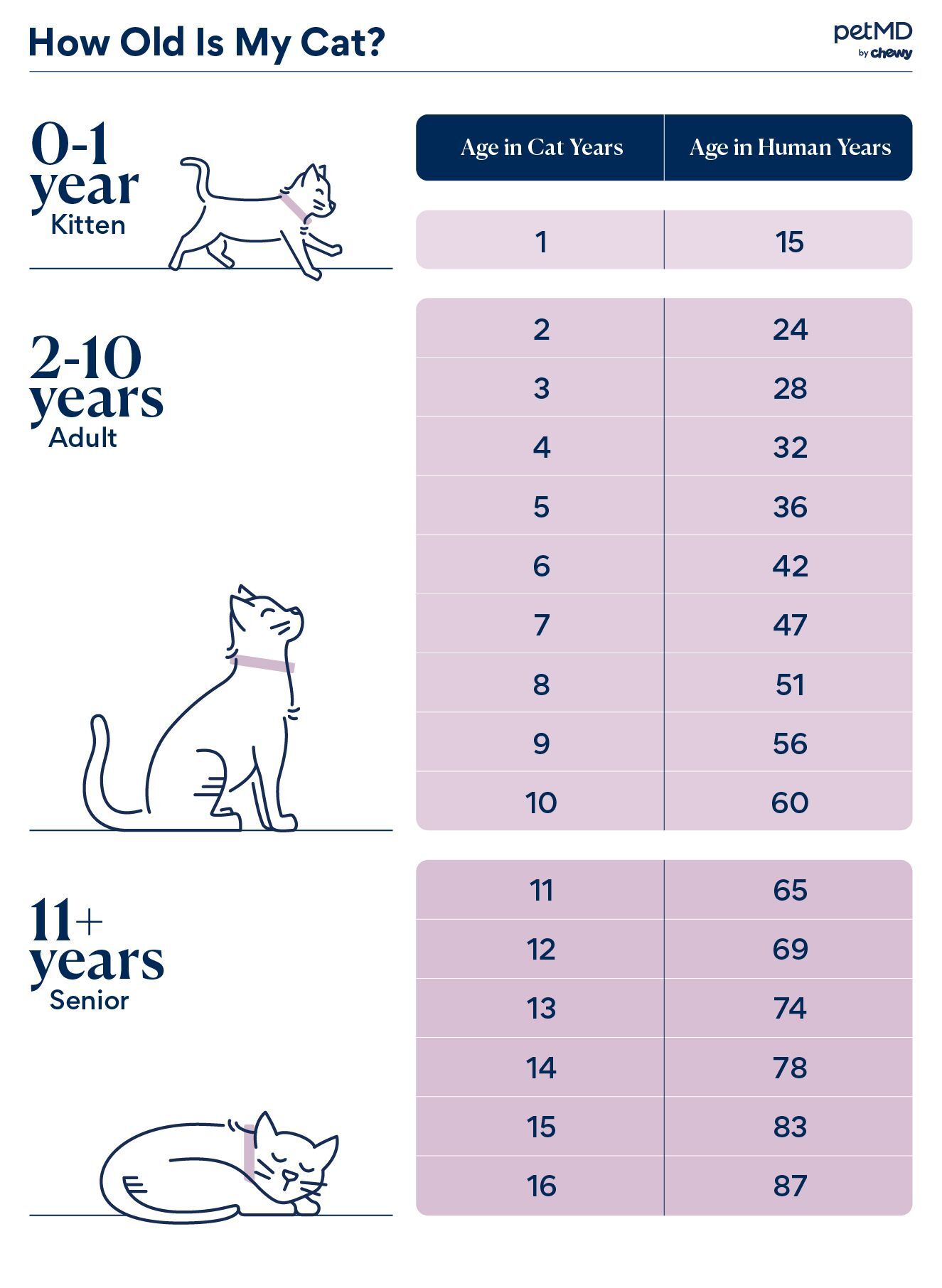
One human year is roughly equal to seven cat years. This is a simplified estimate for understanding a cat’s aging process.
Cats age faster than humans, especially in their early years. By the end of their first year, cats reach the equivalent of a 15-year-old human. In their second year, they age about nine more human years. After that, each additional year equates to roughly four human years.
These conversions help cat owners gauge their pets’ developmental and health needs. Regular vet visits are crucial to address age-related issues. Understanding this helps in providing appropriate care for your feline friend. Proper nutrition, exercise, and mental stimulation are vital for a cat’s well-being throughout its life stages.

Credit: www.rover.com
Introduction To Feline Aging
Cats age faster than humans. Understanding their aging helps in better care. It also helps in predicting health issues. Early detection can save lives. A cat’s first year equals 15 human years. Their second year equals 9 human years. Each year after that equals 4 human years.
Many think one cat year equals seven human years. This is not correct. Cat aging is faster in the first years. Older cats age slower. It’s important to know this for proper care.
The First Year Of A Cat’s Life
Cats grow very fast in their first year. They reach the equivalent of 15 human years. Kittens open their eyes at around 7 to 10 days. By two weeks, they begin to develop their senses.
- At 3 months: Cats start to play and explore.
- At 6 months: Cats reach adolescence.
- At 12 months: Cats are fully grown adults.
Comparing Cat Years To Human Years
A cat’s first year equals 15 human years. The second year adds 9 more human years. Each year after that equals about 4 human years. A 5-year-old cat is like a 36-year-old person. This helps understand their age better.
Indoor cats live longer than outdoor cats. A healthy diet can slow aging. Regular vet visits keep cats healthy. Exercise is also important. Genetics play a big role too. Some breeds age slower than others. Care and love make a big difference.
Credit: www.petmd.com
Life Stages Of Cats
Kittens grow very fast. They reach the age of a human child in just a few months. Kittens are full of energy and love to play. They need a lot of care and attention. Their diet should be rich in nutrients for proper growth.
Adolescent cats are like teenagers. They explore a lot and test boundaries. This stage lasts from 6 months to 2 years. Training and socialization are important during this time. They start to develop their adult personality.
Adult cats are more calm and settled. This stage is from 3 to 6 years. They are active but less playful than kittens. Regular vet check-ups are important. A balanced diet keeps them healthy.
Senior cats are over 7 years old. They may slow down and sleep more. Regular health checks are crucial. Older cats may need special diets. They still need love and attention.
Health And Wellness Across Ages
Cats need different food as they age. Kittens need more calories for growth. Adult cats need balanced food for maintenance. Senior cats need fewer calories but more nutrients. Always choose high-quality cat food. Fresh water is also very important.
Young cats love to play and jump. Older cats may prefer gentle activities. Use toys to keep them active. Climbing trees and scratching posts help them stay fit. Regular playtime keeps them happy and healthy.
Visits to the vet are crucial. Kittens need vaccinations and check-ups. Adult cats need yearly exams. Senior cats may need visits every six months. Early detection of problems helps in quick treatment.
Behavioral Changes Over Time
Kittens are full of energy. They love to play and explore. Everything is new and exciting for them. They often chase toys and pounce on anything that moves. Their playfulness helps them learn. It builds their muscles and coordination. Kittens are curious and adventurous. They can be mischievous at times. Keep them entertained with safe toys. Spend time playing with them. This strengthens your bond.
Adult cats are more independent. They still enjoy playtime but are less active than kittens. They like to explore their surroundings. They often find cozy spots to nap. Adult cats are more self-sufficient. They may not need as much attention. They can be left alone for longer periods. They still enjoy affection from their owners. Regular playtime is still important. It keeps them healthy and happy.
Senior cats are usually calm. They prefer quiet and routine. They sleep more than younger cats. They might not be as playful. They enjoy gentle petting and cuddling. Senior cats need special care. Regular vet check-ups are important. They might need a special diet. Provide them with a comfortable space. Keep their environment stress-free. They still appreciate your love and attention.
Common Health Issues By Age
Young cats often face flea infestations. Regular grooming helps prevent this. Vaccinations are crucial to protect them from diseases. Spaying or neutering can prevent future health issues. Young cats may also develop digestive problems. Feeding them a balanced diet is important.
Middle-aged cats may suffer from dental problems. Regular vet checkups can catch these early. Weight gain is common and needs monitoring. Diabetes can develop in these cats. Arthritis might start showing symptoms. Providing a comfortable place to rest helps.
Older cats often develop kidney disease. Regular vet visits are crucial. Hyperthyroidism is another common issue. Medication can help manage it. Hearing loss might occur in older cats. They may also suffer from vision problems. Ensuring their environment is safe is key.
Enhancing Longevity And Quality Of Life
Regular vet visits are crucial. These visits help detect issues early. Vaccinations and flea control also keep cats healthy. Spaying and neutering can extend a cat’s life. Proper nutrition is another vital aspect. Feed your cat a balanced diet. Avoid overfeeding to prevent obesity.
Toys and games keep a cat’s mind sharp. Interactive play strengthens your bond. Puzzle feeders are great for mental exercise. A stimulated cat is a happy cat. Rotate toys to keep things fresh. New experiences can be exciting for cats.
A cozy bed is essential for a cat’s comfort. Cats love warm and soft places. Ensure the environment is safe. Remove any hazardous items. Provide scratching posts to protect furniture. Clean litter boxes regularly to maintain hygiene. Cats appreciate a quiet space.

Credit: bengalcatworld.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is 1 Year 7 Years For A Cat?
No, 1 year is not equal to 7 years for a cat. Cats age faster in their first two years. After that, they age about 4-5 years per human year.
How Old Is 2 Years For Cat?
A 2-year-old cat is equivalent to a 24-year-old human. Cats age rapidly in their first two years.
How Old Is 3 Years In Cat Years?
A 3-year-old cat is roughly 28 years old in human years. Cats age faster in their first two years.
How Many Years Are In A Cat Year?
A cat year is roughly equivalent to 15 human years for the first year. After that, each year equals about 4 human years.
Conclusion
Understanding cat years helps you care for your feline friend better. Cats age faster in their early years. By knowing their age in cat years, you can provide appropriate health care. Always consult your vet for accurate age-related advice. Cherish each moment with your beloved pet.

Hello, this is Frank Swanson, the owner, and operator of Pet Info Hut. I created this website as a way to share my love of pets with the world. I have over 7 years of experience working with animals, and I have a passion for helping people care for their pets. I hope that you find my website useful and informative. Thanks for visiting!
